Hajj and ‘umrah glossary
Adhan – the call to prayer.
Afaqi – Pilgrim who comes from outside the appointed miqats.
Ahadith – Plural of hadith.
Aswad – black.
Ayyaam – days.
Ayyaam al- Tashriq – Literally means ‘the days of drying meat.’ The 11th, 12th and 13th of Dhul-hijja during which pilgrims stay in Mina, and perform the rites of throwing pebbles.
Arafat – a plain 15 miles to the east of Makkah on which stands the Jabl al-Rahma, the Mount of Mercy, where it is said Adam was re-united with Hawwa (Eve) after years of wondering following their expulsion from the Garden of Adn (Eden). One of the essential rites of the Hajj is to stand on Arafa on the 9th of Dhul Hijja.
Aurah – Parts of the body that must be covered.
Asr – The afternoon prayer (salah).
Ashura – The tenth day of Muharram.
Barakah – Blessing of Allah.
Badal – Substitute.
Al-Bayat- al-Haram – The Ka’ba in Makkah (This name was given to it because of the prohibition of hunting inside it or around it).
Baqi – the cemetery of the people of Madinah where many of the family of the of Messenger Allah (PBUH) and his companions are buried.
Bida – Innovation.
Dhikr – Remembrance of Allah.
Du’a – Supplication, invocation.
Dumm – Blood. The word is used by the jurists for atonement by sacrificing an animal, usually in the case of violation of a wajib act of hajj.
Dhul-hijja – The twelfth month of the Islamic calendar, the month of the Hajj (pilgrimage).
Dhul Hulayfa – The miqat of the people of Madina, now near Bayar Ali.
Dhu mahram – A relative of the prohibited degree of marriage.
Eid al-Adha – A four day festival at the time of Hajj. The Eid of the sacrifice starts on the 10th day of Dhul-Hijja, the day that the pilgrims sacrifice their animals in the name of Allah. An animal such as a sheep or goat is sacrificed as a commemoration of Prophet Ibrahim’s (pbuh) willingness to sacrifice his son for God.
Eid al-Fitr – The festival at the end of the month of fasting (Ramadan).
Ezaar – Lower cloth of Ihram.
Fidyah – Literally means ransom. It is compensation paid for rites missed or wrongly performed because of ignorance or ill-health.
Fiqh – Islamic jurisprudence. Fiqh is knowledge of the law as distinguished from shariah, which is the law itself.
Fard – An obligation established by definitive evidence.
Fuqaha –Jurists; expert in fiqh.
Ghusl – The full ritual washing of the body.
Hady – An animal offered as a sacrifice during the Hajj.
Hajj – Literally means ‘to set out for a place’; annual pilgrimage to Makkah.
Hajj al Ifrad – The type of hajj where the pilgrim pronounces his or her intention to perform only Hajj at Miqat while changing into Ihram.
Hajj al Qiran – The ‘joined’ hajj, where the pilgrim pronounces his or her intention to perform both ‘Umrah and Hajj together with the same Ihram at Miqat.
Hajj al Tammattu – The ‘interrupted’ hajj, where the pilgrim pronounces his or her intention to perform only ‘Umrah at Miqat when assuming Ihram. A second niyyah, and a second change into Ihram follow on the 8th of Dhul Hijjah for the performance of the remaining rites of Hajj.
Hajr al Aswad – The sacred Black Stone built into the south-east corner of the Ka’ba at a height of approximately four feet from which pilgrims begin the Tawaf .
Halal – Permitted.
Halq – The complete shaving of the head by the male pilgrim on the 10th of Dhul Hijjah. This is the last thing he does before leaving the state of Ihram. For female pilgrims, the requirements of Halq and Taqseer are satisfied if they trim their hair by approximately half an inch.
Haramain – The two sacred mosques in Makkah and Medina.
Haraam – Forbidden, prohibited.
Hijaz – the region along the western seaboard of Arabia, in which Makkah, Medina, Jeddah and Ta’if are situated.
Hijr – the semi-circular unroofed enclosure at one side of the Ka’ba, whose low wall outlines the shape of the original Ka’ba built by Prophet Ibrahim (AS).
Hijra – to emigrate in the way of Allah. Islam takes its dating from the Hijra of the Prophet (PBUH) to Madinah.
Ibada – act of worship.
Idtiba – The mode of Ihram used during ‘Umrah Tawaf and Tawaf al Qudoom. The male pilgrim drapes one end of the top part of his Ihram over his left shoulder back-to-front. The other end goes across his back, under his right arm, across his front, and is finally draped over his left shoulder. Idtiba is not observed in any other type of Tawaf.
Ifadah – Refers to the Tawaf performed by a pilgrim when she/he comes from Muzdalifah.
Ihram – Ihram literally means forbidding; here it signifies the intention to enter into the performance of the rites of Hajj or Umrah, or both. The term is also used to denote the Pilgrim’s habit worn on occasion of the hajj, and the state in which the Pilgrim has to remain until he lays aside the garb. The distinctive garb of the pilgrim consists of two pieces of white, plain and unsewn cloth for the male. One of the pieces (lower part) is wrapped around the midriff to cover his body from just above his navel to below his ankles, and the other (upper part) is draped around his shoulders to cover the upper body, and sometimes exposing the right shoulder of the male pilgrims. For ladies, ordinary, and unpretentious clothes of daily wear constitute their Ihram.
Iqama – the call which announces that the obligatory prayer is about to begin.
Istislam – Literally means submission but here refers to the greeting of the Black Stone and Yemeni corner of the Ka’ba during tawaf by kissing, touching or outstretched hand.
I’tikaf – seclusion, in a mosque paricularly in the last ten days of Ramadan.
Jamra (plural jamarat)- Literally a small walled place, but meant here a stone-built pillar and in particular the three stone pillars in Mina which symbolically represent the locations where the devil (shaytan) attempted to tempt Prophet Ibrahim (pbuh) away from the path of Allah. The pilgrim symbolically stones these pillars on the 10th through to the 13th of Dhul Hijjah in commemoration of the rejection of the devil by Prophet Ibrahim, and of his steadfastness to the cause of Allah.
Jamrat al Aqaba – The location at which pebbles are to be cast during pilgrimage, especially on the 10th of hajj. It is situated at the entrance of Mina from the direction of Makkah.
Jamrat al Ula – The first stone pillar in the line.
Jamrat al Wusta – The second (middle) stone pillar in the line.
Janaba – The state of impurity in which a person requires ghusl.
Ji’rana – a place near Makkah, when the Messenger of Allah (PBUH) distributed the booty from the Battle of Hunany and from where he went into ihram to perform ‘umrah.
Al-Juhfa – the Miqat of the people of Syria and Europe.
Jumu’a – the Day of Gathering, Friday, and in particular the Jumu’a prayer.
Ka’ba – A cubic structure originally built by Prophet Ibrahim (pbuh) and his eldest son Ishmael. During Hajj, the essential rite of Tawaf is performed around the Ka’bah.
Kaffara – prescribed way of making amends for wrong actions, particularly missed obligatory actions.
Khutba – literally a speech, and in particular the addresses given by the Imam on the day of Jumu’a and the two Eids.
Kiswat – The clothes that covers the Ka’ba.
Labbayk – A call meaning “Here I am at Thy service”. It is the Muslim’s expression of answering the invitation of Allah to perform pilgrimage.
Madhab – a school of thought(fiqh). There are four main sunni madhabs : Hanafi, Maliki, Shafi’i and Hanbali.
Mahram – a person with whom marriage is expressly prohibited by the shariah (e.g., father, brother, uncle, nephew, etc.) A woman must be accompanied by a Mahram for Umrah and Hajj.
Makruh – disapproved, reprehensible.
Maqam Ibrahim – The stepping stone used by Prophet Ibrahim (pbuh) during the original construction of the Ka’bah. The stone carries the imprints of his feet, and is housed in a glass enclosure on the north side of the Ka’ba. It marks the place of prayer following tawaf of the Ka’ba.
Marwah – A rocky hillock located approximately 250 meters northeast of the Ka’ba inside Al Masjid al Haram. It is the hill on which a pilgrim ends his or her Sa’i. The pilgrim performs the devotional rite of Sa’i between the hillocks of Safa and Marwah.
Al-Mashar – The Valley between Muzdalifa and Mina, where pilgrims should make a Du’a after they have slept in Muzdalifah while they are going to Makkah to throw Jamrat al-Aqabah on the morning of the 10th of Dhul-Hijjah.
Masjid al Haram – The Protected Mosque, the name of the mosque built around the Ka’ba in the Haram at Makkah.
Mihrab – The place where the Imam stands during congregation salah.
Mimbar – The place where the Imam stands while delivering a khutbah (sermon).
Mina – A desert location approximately three miles east of Makkah on the road to Arafah where several rites of Hajj are performed.
Miqat (Plural Mawaqit) – The place where Muslims declare their intention to make Hajj or Umrah and begin the state of Ihram. A prospective pilgrim cannot cross the Miqat boundary without first changing into Ihram. This boundary is anchored by different townships and localities in different directions.
Muhrim – A pilgrim in the state of Ihram.
Multazam – The part of the Ka’ba between its door and Hajar al Aswad.
Mutamatti – A person undertaking the Tamattu form of hajj.
Muzdalifah – A place between Arafa and Mina where the pilgrims spend a night in the open on their return from the station at Arafat.
Namira – A mosque in Arafat.
Nafl – literally a gift. It means a voluntary act of worship.
Niqab – the face veil adorned by Muslim women.
Niyyah – Intention. All acts of worship are preceded by an appropriate niyyah.
Qarin – A person undertaking the Qiran form of hajj.
Qasr – The mode of shortened prayers usually offered when on a journey.
Qibla – The direction faced in Prayer, which is towards the Ka’ba in Makkah.
Quba – a village on the outskirts of Madina.
Rakah – a unit of prayer.
Raml – ‘hastening’ in the tawaf, a way of walking briskly, moving the shoulders vigorously. Ladies are not required to practice Raml.
Reda – The upper cloth of Ihram.
Ramy – The act of symbolically stoning the devil in Mina on the 10th through to the 13th of Dhul Hijjah.
Sadaqa – Anything given voluntarily in charity.
Safa – A small hillock approximately 200 m southeast of the Ka’bah, inside Al Masjid al Haram, on which a pilgrim begins his or her Sa’i.
Sa’i – The walk made between Safa and Marwah.
Salat – Obligatory or supererogatory prayers. It consists of fixed sets of standing s, bowings, prostrations and sittings in worship to Allah.
Shawt – One complete circumambulation, or circuit, of the Kabah. Each shawt (pl. ashwaat) starts and ends at Hajar ul Aswad. Seven ashwaat constitute one Tawaf.
Shaytan – a devil particularly Iblis (Satan).
Talbiyah – A recital of the following words by the pilgrim during ‘Umrah and Hajj: Labbaik Allahumma Labbaik. Labbaik, La Shareek Laka, Labbaik. Innal Hamdah, Wan Nematah, Laka wal Mulk, La Shareek Laka Translation: “Here I am at Thy service O Lord, here I am. Here I am at Thy service and Thou hast no partners. Thine alone is All Praise and All Bounty, and Thine alone is The Sovereignty. Thou hast no partners.” The Talbiyah is a prayer as well as an assertion of the pilgrim’s conviction that he or she intends to perform Hajj only for the glory of Allah. The pilgrim starts the recital upon changing into the Ihram, and continues to recite it frequently throughout Hajj. Male pilgrims recite the Talbiyah loudly whereas female pilgrims are required to recite it in a low voice.
Tahallul : Freedom from the restrictions of the ihram. It is of two types: full freedom (tahallul akbar), which occurs after tawaf-al-Ifada, and partial freedom (tahalull asgar), which occurs after casting of pebbles at the Jamarat al-Aqaba.
Tamattu – The type of Hajj where a pilgrim starts with Umrah then makes Hajj later on but in the same year.
Taqsir – Shortening or clipping of the whole head of hair by the male pilgrim following the completion of Hajj. This may be performed in lieu of Halq.
Tarwiyah – The 8th day of Dhul-Hijjah.
Tashriq – Days following the day of sacrifice (The 11th, 12th, and 13th days of Dhul-Hijjah).
Tawaf – The seven fold circumambulation of the Ka’ba while reciting prayers. It constitutes an integral part of ‘Umrah and Hajj. There are five different types of Tawaf (see Tawaf chapter).
Tawaf al Ifadah – The obligatory Tawaf of the Ka’ba during hajj after throwing pebbles at the jamarat. It is also known as tawaf al-ziyara.
Tawaf al Nafl – A devotional Tawaf which may be performed any time.
Tawaf al Qudoom – The initial Tawaf performed by the pilgrim coming from outside Makkah.
Tawaf al ‘Umrah – The Tawaf performed as a rite of ‘Umrah.
Tawaf al Wida – The Farewell Tawaf performed by the pilgrim just before leaving Makkah for his or her next destination.
‘Umrah – A visit to the House of Allah in a state of ihram. ‘Umrah, or lesser Hajj, includes Tawaf and Sa’i, but unlike Hajj, does not involve the rites at Mina, Muzdalifah, and Arafat.
Udhiya – Sacrifice of an animal for Allah on the day of Eid-ul-Adha.
Wuquf – Literarily means standing or staying in Arafat (on the 9th of Dhul-hijja). It is a central rite of Hajj.
Wudhu – The ritual ablution usually performed prior to prayer.
Yaum al Nahr – The 10th of Dhul Hijjah. This day is designated as the preferred day of sacrifice during Hajj.
Yaum al Tarwiyah – The 8th of Dhul Hijjah signifying the start of Hajj. The pilgrim proceeds to Mina on this day.
Zamzam – The name of the sacred well of water which sprang forth miraculously under Prophet Ishmael’s (pbuh) feet as an infant.
Zawaal – when the sun is at its zenith, midday.
When at Mount Safa and Mount Marwah
Jaabir (radhi-yAllaahu ‘anhu) said when describing the Prophet’s (sal-Allaahu ‘alayhe wa sallam) pilgrimage, when he (pbuh) approached mount as-Safaa he would recite:
إِنَّ الصَّفَا وَالْمَرْوَةَ مِنْ شَعَآئِرِ اللَّهِ
Inna assafa walmarwatamin shaAAa-iri Allahi
Indeed, as-Safa and al-Marwah are among the symbols of Allah
…and then say:
أَبْدَأُ بِمَا بَدَأَ اللَّهُ بِهِ
Abda’u bimaa bada’allaahu bihi.
…so he started with as-Safaa and climbed it until he could see the Ka’bah, he then faced it and said:
لاَ إِلَهَ إِلاَّ اللَّهُ وَحْدَهُ لاَ شَرِيكَ لَهُ، لَهُ الْمُلْكُ وَلَهُ الْحَمْدُ وَهُوَ عَلَى كُلِّ شَيْءٍ قَدِيرٌ، لاَ إِلَهَ إِلاَّ اللَّهُ وَحْدَهُ، أَنْجَزَ وَعْدَهُ، وَنَصَرَ عَبْدَهُ، وَهَزَمَ الْأَحْزَابَ وَحْدَهُ
Laa ‘ilaaha ‘illallaahu wahdahu laa shareeka lahu, lahul-mulku wa lahul-hamdu wa Huwa ‘alaa kulli shay’in Qadeer, laa ‘ilaaha ‘illallaahu ilahaahu, ‘anjaza wa’dahu, wa nasara ‘abdahu, wa hazamal ‘ahzaaba wahdahu.
None has the right to be worshipped but Allah alone, Who has no parener, His is the dominion and His is the praise, and He is Able to do all things. None has the right to be worshipped but Allah alone, He fulfilled His Promise, He aided His slave, and He alone defeated Confederates.
Ref: Muslim 2/888.
The Day of ‘Arafah
The Prophet (pbuh) said, “The best of supplications is the supplication on the day of ‘Arafah and the best which I and the Prophets before me have said” is:
لاَ إِلَهَ إِلاَّ اللَّهُ وَحْدَهُ لاَ شَرِيكَ لَهُ، لَهُ الْمُلْكُ وَلَهُ الْحَمْدُ وَهُوَ عَلَى كُلِّ شَيْءٍ قَدِيرٌ
Laa ‘ilaaha ‘illallaahu wahdahu laa shareeka lahu, lahul-mulku wa lahul-hamdu wa Huwa ‘alaa kulli shay’in Qadeer.
None has the right to be worshipped but Allah alone, Who has no parener. His is the dominion and His is the praise, and He is Able to do all things.
Ref: At-Tirmithi. Al-Albani graded it good in Sahih At-Tirmithi 3/184, and also Silsilatul-‘Ahadith As-Sahihah 4/6.
Most searched
 Hajj and ‘umrah quiz – test yourself to see how prepared you are for hajj and ‘umrah.
Hajj and ‘umrah quiz – test yourself to see how prepared you are for hajj and ‘umrah.
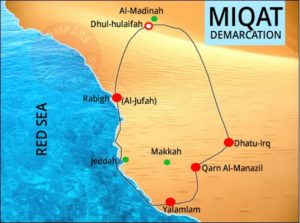 What is miqat and rulings on miqat? – The literal meaning of miqat is “a stated time or place.”
What is miqat and rulings on miqat? – The literal meaning of miqat is “a stated time or place.” Step by step guide to Tamattu hajj – Tamattu hajj consists of both hajj and umrah.
Step by step guide to Tamattu hajj – Tamattu hajj consists of both hajj and umrah.
